
CR VAWT wind turbines reimagined - Why
| HOME | OUR COMMUNITIES | MANUFACTURING | WHY CR VAWTs | EXPERIENCE |
According to research developed for the Asian Development Bank; Vertical axis wind turbines are an indispensable type of wind energy technology, which have not yet been fully utilized.
https://www.adb.org/publications/appropriate-technologies-removing-barriers-expansion-renewable-energy-asia#
"Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs)
account for the bulk of grid-connected wind turbines, but are expensive,
gigantic, difficult to install, operate, repair and maintain, and require a
large area of land for their operation. They need fast winds to generate power
that is not available all the time and have to be shut down during strong winds
that are above their “survival speed.” Since they are intermittent sources of
power generation, they consequently require backup generators, and these
generators usually emit carbon dioxide. Given this reality, it could be
concluded that wind turbines are an inappropriate means of power generation, but
it is HAWTs, rather than all wind turbines, that have major negative features,
making them an inappropriate choice for large-scale power generation, despite
their benefits."
"Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) are a solution, but they are not yet widely
used, and their technology needs further development to address their
shortcomings. VAWTs operate with slower wind speeds than the required minimum
speed of HAWTs, and with very fast winds. VAWTs are much cheaper and easier to
build, install, operate, repair and maintain than HAWTs, do not require a large
area of land, and can be installed near each other, in between HAWTs and in
urban areas."
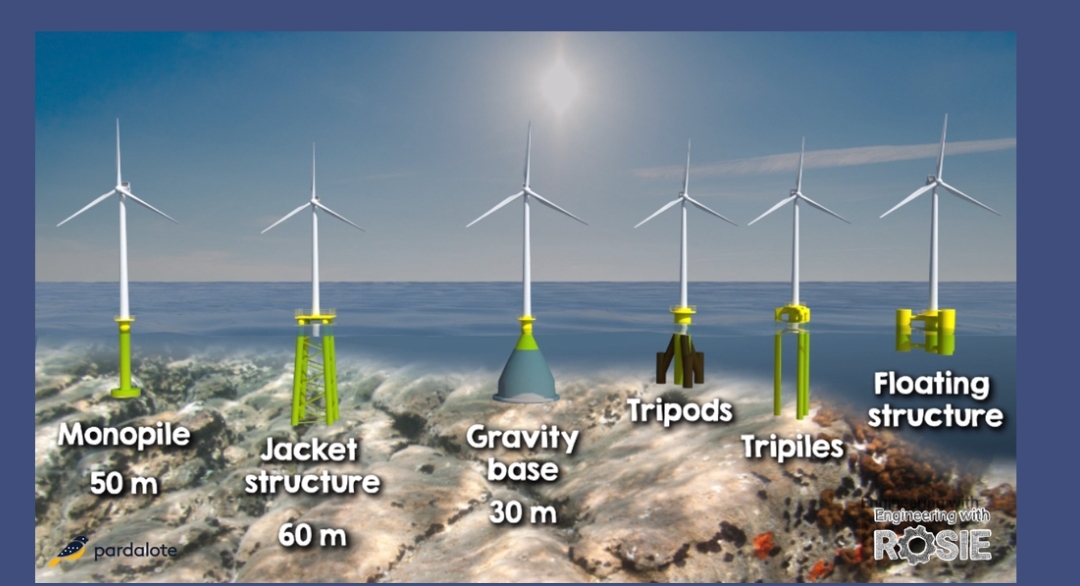
Roughly 80% of the world’s offshore wind
resources are located in waters too deep for regular offshore wind turbines,
according to the Global Wind Energy Council, a forum representing the wind
sector. By investing in floating offshore wind, more renewable power generation
can be harnessed, as the turbines are able to operate in deeper waters where
there is more wind.
“Floating offshore wind technology accesses these strong winds and unlocks the
possibility of building more much-needed clean power,”
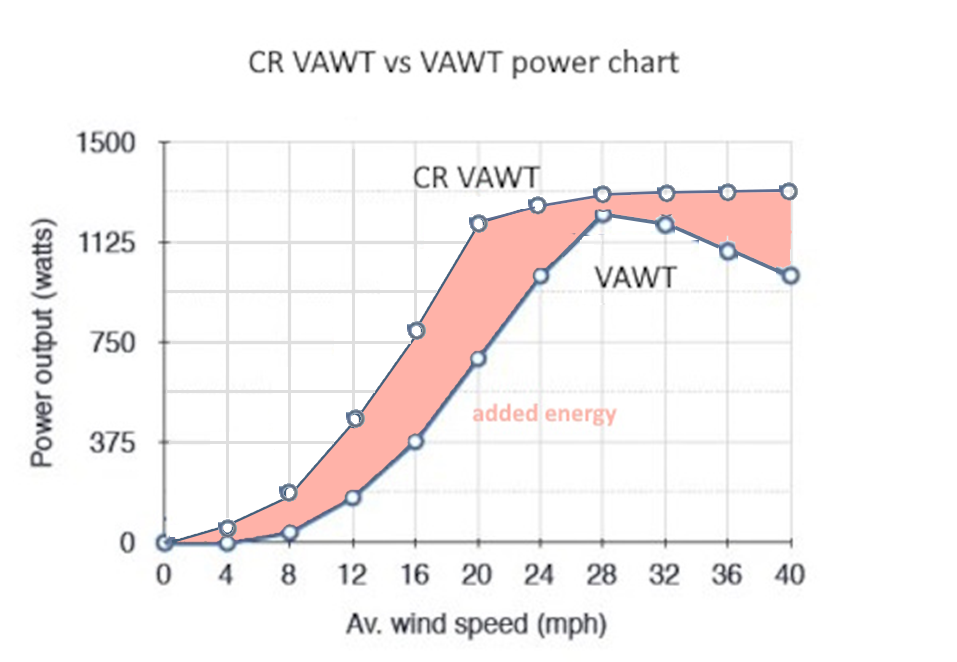
We can install 3 CR VAWTs on each semi-submersible which further enhance it's productivity!

Semi-submersible CR VAWT 24MW arrays (below) offer significant advantages over conventional HAWTs!
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/11/offshore-wind-farms-future-renewables/
Why CR VAWTs:
Reduce wildlife mortalities.
Low noise.
Arrays allow high density of turbines near existing infrastructure.
9 x better reliability and longevity than a conventional generator.
Low stress blades in VAWT configuration ensures increased service life and
reliability.
A
CR VAWT will have >double the service life to a HAWT!
1. The configuration of the CR VAWT
Allows the rotor and stator to rotate in opposite directions, doubling the
actual wind speed and energy output without the need for a gearbox. This feature
allows the CR VAWT to have a world leading turbine efficiency of 56% (20% more
than HAWTs) and generator efficiency of 98%
Research shows that there are a few characteristics and advantages of vertical
axis wind turbines that make them perfect choices for certain geographical
conditions and wind energy applications.
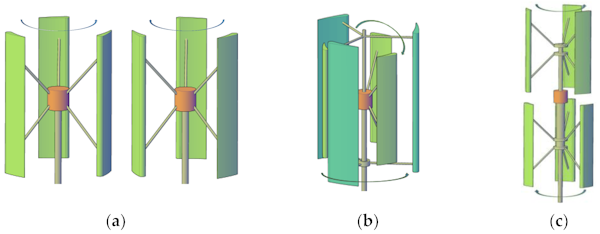
Four different CR VAWT configurations (above)
2. Omnidirectional nature of the Rotor
Vertical axis wind turbines can pick up wind coming from any direction.
Horizontal axis wind turbines need to face the direction of the wind to operate,
and rely on a mechanical yaw system to orientate the rotor in order to capture
wind.
Due to this difference in operation mechanism, vertical axis wind turbines can
be used to generate power even in unstable weather conditions such as turbulent,
gusty wind. They function well in city, mountain and coastal areas.
3. Optimal land use
In a horizontal axis wind turbine farm, the general rule-of-thumb for spacing is
to place the turbines 5 diameters apart across the wind, and about 10 diameters
apart extending downwind. This is to avoid disruption of air flow and reduction
in wind speed caused by one turbine to another, which affects the power output
of neighboring units.
Compared to horizontal axis wind turbines, vertical axis wind turbines can be
grouped closer together in a wind power plant. This is because vertical axis
wind turbines function well in turbulent wind. They are generally spaced 4 to 6
diameters apart.
Closer spacing would allow a wind power plant to capture more energy per square
meter of land. Generally speaking, a single vertical axis wind turbine is not as
energy-efficient as an individual horizontal axis wind turbine. However, a group
of closely-spaced vertical axis wind turbines have the potential to generate as
much as 10 times more power per unit of land compared to a group of
widely-spaced horizontal axis wind turbines.
This also applies to underutilised land in transmission corridors and in
suburbia. Horizontal axis wind turbines requires a large area of land to allow
it a 360 degree turning area. Whereas vertical axis wind turbines can be placed
adjacent to buildings, trees or another turbine.
4. Lower Starting Wind Speed
Vertical axis wind turbines have a lower starting wind speed compared to the
horizontal axis models. The necessary starting wind speed for a typical vertical
axis wind turbine is 2 to 3 m/s. This allows vertical axis wind turbines to
generate electricity even when incoming wind is relatively weaker. Although the
amount of electricity generated at lower wind speeds is small, it makes a lot of
energy available when other wind turbines are not able to harvest at all!
5. Lower Environmental Harm
Generally smaller, the size of vertical axis wind turbines brings along a few
advantages, one of which being low environmental harm. The blades are easier to
spot for birds and other flying animals, decreasing the chance of animal
casualty.
Vertical axis wind turbines spin more slowly, thus operate with quieter noise
emission, so they do not disturb people at work or in residential neighborhoods.
6. Easier Installation and Maintenance
The smaller size of vertical axis wind turbines makes them easier to transport,
set up, and maintain. For example, all parts of one 12kW turbine can be
delivered with a single truck with a 6-meter long storage space. Maintenance
workers do not have to climb as high to reach parts of the turbine because the
major components, such as the generators, are built closer to the ground. Farste
Drives have 9 x better reliability and longevity than a conventional generator.
Low stress blades in VAWT configuration ensures increased service life and
reliability. CR VAWT will have double the service life to a HAWT =less waste and
$$ savings!
7. Less Restricted Installation
Being safer to wildlife and quieter than horizontal axis wind turbines our
turbines can be can be erected close to dwellings and existing infrastructure,
even integrated into lighting poles/towers, telecommunication towers and
neighborhood batteries. And mounted on skids that can be sited on existing
buildings, or where soil conditions won’t allow standard foundations. Solar
needs vast amounts of land and HAWTs need to be located away from populated
areas.
Rather than spend $Billions constructing transmission lines to reach isolated
wind and solar farms we can site CR VAWTs in transmission corridors and on
existing buildings.
Off-shore CR VAWT wind farms near population centres offer the lowest infrastructure cost, the lowest resources use, the lowest visual impact and the least harm to all of earth's creatures!
8. Striking Representation
The modern geometrical designs of vertical axis wind turbines allow them to
operate with elegance and create smooth visual flow. Their appearance is
complementary to buildings, campuses, and parks. Utilising wind power to
generate electricity, they also speak directly about the sustainable values of
an organization or community with strong visual impressions.
9. Generators
CR VAWT have licenced the Farste Drive (image below) TOROID PCB RADAX electric
motor/generator to provide the generator. The Farste Drive has no copper
windings as per a traditional electric motor; instead uses multi-layered Printed
Circuit Boards (PCBs) that replicate the properties of copper windings.
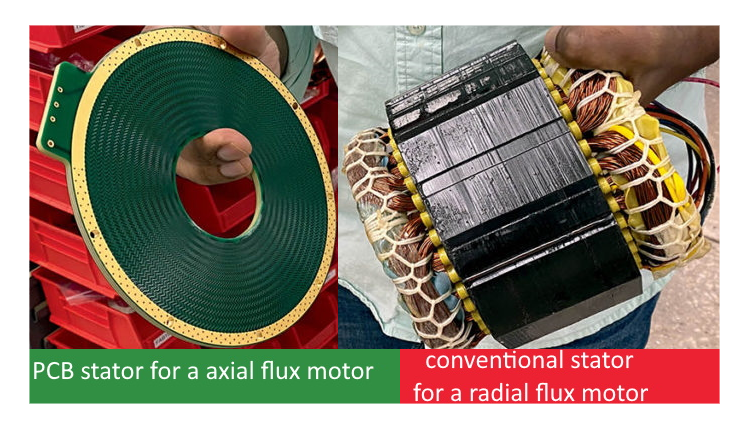
| copyright NTWTF.com 2024 |